Published on: Nov 1, 2023
Understanding KPIs, KRIs, and Metrics within GRC - Measuring Your Organization's Growth
As you strive to strengthen compliance and risk management, a foundational understanding of KPIs and KRIs is non-negotiable.
This article offers clear, concise insights to enhance your understanding of metrics within the GRC and how they impact decision-making.
Let's get started!
Understanding Data-Driven Organizations
In today's digital landscape, data-driven organizations are leading the way. For these companies, data isn't just a trend - it's the foundation of their success.
At its heart, these organizations collect streams of data from every corner of their operations, and, at the same time, they foster a culture where employees embrace data literacy to make decisions.
These organizations emerge as digital champions, agile and adaptable, always staying one step ahead in protecting their assets, mitigating risks, and better controlling their internal processes.
In this context, data is the key to unlocking smart Governance, Risk, and Compliance practices.
How do they do it, though?
The data they collect is used in compliance metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and the organization's ability to keep its processes in line with the different standards, regulations, rules, and its own policies.
The Requirement Arises From Standards
The use of data to track and improve compliance performance might sound new and very driven by digital transformation. However, the concept of building KPIs (or objectives) is at the core of the most well-known standards.
Several information security standards and frameworks emphasize the importance of tracking objectives and performance metrics to ensure effective cybersecurity practices:
ISO/IEC 27001 - Information Security Management System (ISMS): ISO 27001 requires organizations to establish an ISMS, which includes setting information security objectives to improve their programs and practices. These objectives must be measurable and aligned with the organization's overall business goals. Regular monitoring and measurement of the objectives' performance are essential components of ISO 27001 compliance.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: NIST CSF encourages organizations to establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure their cybersecurity performance. One of its core functions is the "Measure" function, which focuses on establishing and tracking performance metrics to gauge the effectiveness of cybersecurity activities.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): To ensure compliance, organizations are required to establish security objectives and key performance indicators related to the protection of payment card data. Regular tracking and reporting on these metrics are essential for maintaining compliance and reducing the risk of data breaches.
Information security standards and frameworks require organizations to establish and track security objectives, metrics, and key performance indicators.
These requirements are integral to ensuring that organizations continuously improve their information security practices and remain compliant with industry-specific and regulatory standards.
Now, let's clarify some concepts.
What are KPIs? (Key Infosec Performance Indicators for Infosec Professionals)
Key Performance Indicators, commonly referred to as KPIs, are quantifiable measurements that help organizations track their performance against specific objectives. These indicators provide insights into how well a company is achieving its operational and strategic goals.
When it comes to measuring things in compliance, more specifically in information security, there is a multitude of Key Performance Indicators that can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your compliance program.
Here are some key types of KPIs, along with examples:
Incident Resolution Time: This KPI tracks the average time it takes to resolve compliance-related incidents. For instance, if there's an issue related to data breaches, measuring how quickly your team responds and resolves the situation can be crucial.
Policy Adherence Rate: This KPI assesses how well employees adhere to company policies and procedures. For example, it can measure the percentage of employees who complete mandatory compliance training, or you can track the number of non-conformities within a time period.
Risk Assessment Scores: Measuring risk levels associated with different areas of your organization can be vital. By assigning scores to various risks and tracking them over time, you can prioritize actions in areas with higher risks.
Compliance Audit Findings: This KPI monitors the findings of compliance audits and assessments. It helps identify areas where your organization consistently falls short in meeting compliance standards.
Third-Party Compliance: For organizations that work with third-party vendors or partners, tracking their compliance can be critical. Monitor their adherence to contractual agreements and regulations.
Characteristics of KPIs:
Relevance: Directly tied to organizational goals and objectives.
Quantifiable: Can be measured in numbers, percentages, or other metrics.
Actionable: Offer insights that lead to corrective actions or strategic shifts.
Time-Bound: Measure performance within a specified timeframe.
Let's take a look at KRIs now.

Key Risk Indicators (KRI) and its Pivotal Role
While KPIs measure the achievement of objectives, KRIs act as safeguards, ensuring potential risks are identified and managed.
KRIs are specific metrics or data points used in risk management to assess and monitor potential risks or vulnerabilities within an organization.
Unlike Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which focus on measuring the overall performance and success of an organization's objectives, KRIs are primarily concerned with identifying and tracking key risks that could impact an organization's ability to achieve its objectives.
Here are some key characteristics and purposes of KRIs:
Risk Identification: KRIs are used to identify potential risks or vulnerabilities that could affect an organization's operations, finances, reputation, or compliance with regulations.
Early Warning Signals: They serve as early warning signals, allowing organizations to detect and respond to emerging risks before they escalate into significant issues or crises.
Quantifiable Metrics: KRIs are typically quantifiable and data-driven, making them objective measures of risk. They are often based on historical data, benchmarks, or industry standards.
Monitoring and Reporting: Organizations regularly monitor and report on KRIs to track the status of identified risks. If a KRI exceeds a predefined threshold, it can trigger risk mitigation or management actions.
KRIs can vary widely depending on the nature of the organization and its specific risks. In cybersecurity, the number of vulnerabilities in a system, security breaches or incidents, malware infection rate, and time to detect and respond to security incidents can all be used as indicators.
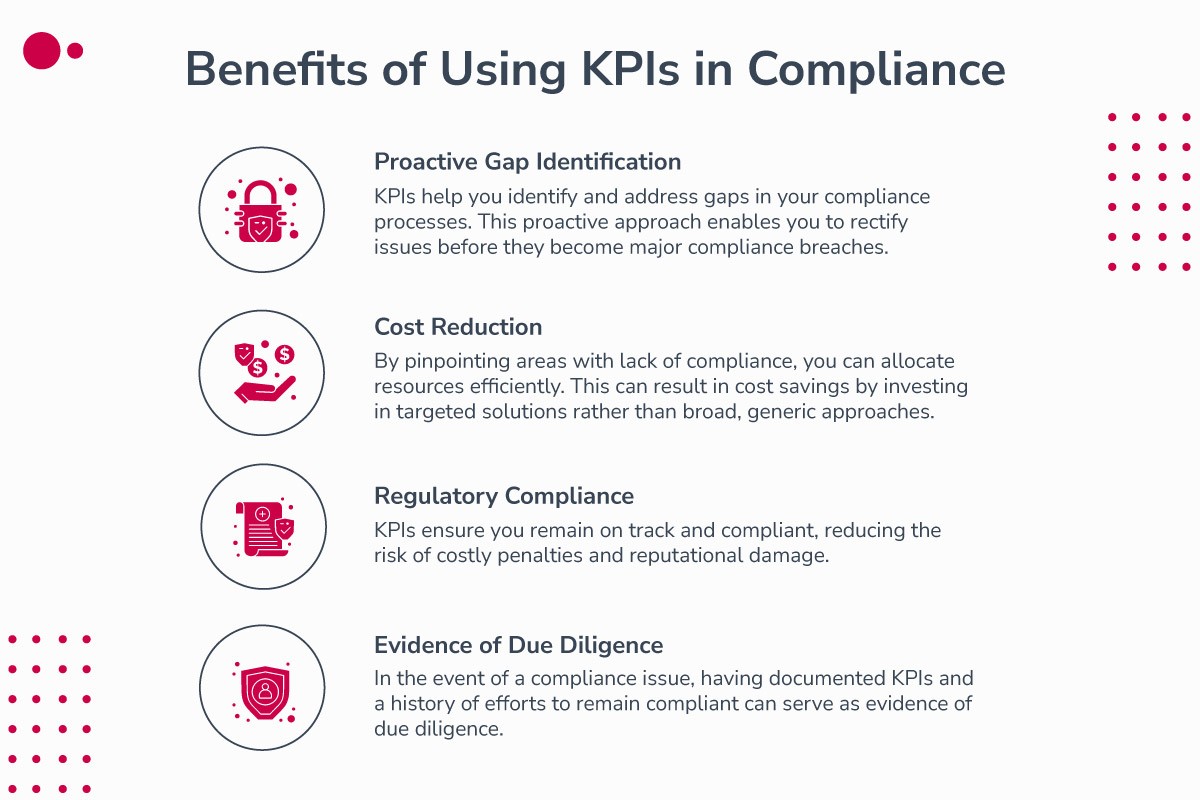
Benefits of Using KPIs in Compliance
Using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in information security compliance is like having a secret weapon in your cybersecurity arsenal.
First off, it's all about keeping your digital fortress strong and secure. KPIs help you measure and track the effectiveness of your security controls, ensuring they're working as they should be.
Here are the advantages of using KPIs:
Proactive Gap Identification: As mentioned earlier, KPIs help you identify and address gaps in your compliance processes. This proactive approach enables you to rectify issues before they become major compliance breaches.
Cost Reduction: By pinpointing areas where compliance is lacking, you can allocate resources more efficiently. This can result in cost savings by investing in targeted solutions rather than broad, generic approaches.
Regulatory Compliance: In a dynamic regulatory landscape, staying current with changes can be daunting. KPIs ensure you remain on track and compliant, reducing the risk of costly penalties and reputational damage.
Evidence of Due Diligence: In the event of a compliance issue, having documented KPIs and a history of efforts to remain compliant can serve as evidence of due diligence. This can be crucial in demonstrating your commitment to regulators and authorities.
In a nutshell:
KPIs are indispensable tools for Compliance Directors and Information Security Managers. They not only help you monitor and improve your compliance efforts but also provide valuable evidence of your commitment to regulatory compliance, reducing potential risks and liabilities.
By leveraging the right KPIs, you can transform compliance from a mere checklist to a strategic advantage for your organization.
KPIs, KRIs, and Metrics Final Thoughts
In this journey through the world of data-driven organizations, compliance, and risk management, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be used as trusty metrics that help keep the digital fortresses strong and secure.
From incident resolution times to policy adherence rates, KPIs serve as our vigilant watchdogs, ensuring we stay on top of compliance and risk.
Organizations that are willing to take a proactive approach to managing compliance and being more efficient, with minimal waste of resources and time, should care about KPI and KRI.
It's not just about playing the compliance game; it's about winning it.
Using KPIs, you can spot gaps in your processes, reduce costs, stay compliant with ever-changing regulations, and prove your due diligence to auditors.
These indicators can be a powerful weapon in the cybersecurity arena and digital transformation. Using them as a strategic advantage can guarantee a secure, compliant, and successful digital future.
Are you curious about how to seamlessly integrate KPIs and KRIs into your risk and compliance strategy?
Connect with our team to discover the potential of strategic, data-driven compliance and see first-hand how StandardFusion can enhance your risk and compliance initiatives with a targeted approach.
Prepare your organization for enduring success in a digital world.