Published on: Dec 16, 2023
Strategizing Compliance Automation: What You Should Do to Automate Compliance
In the last article of this series, we answered "Why should you consider Compliance Automation?." We discussed the following topics:
How teams can gain efficiency by automating workflows
How automated auditing and reporting can help save time and reduce costs
How real-time monitoring and evidence gathering can be game-changing.
Cost saving through automation
In this second article, we will articulate around "What should you do to automate compliance?." We will unveil the scope of work for organizations willing to kick off Compliance Automation Projects and expand a bit further on the topics of data collection and audit preparation.
Defining the Scope
Strategic Compliance decisions often start with important questions around scoping. Scope refers to the totality of the work or services that need to be accomplished to achieve the project's objectives and deliverables.
In the context of Governance, Risk, and Compliance, "scope" refers to the extent or boundaries within which an organization's information security policies, processes, controls, and compliance efforts are applied. Furthermore, defining the scope is essential to ensure that compliance efforts are appropriately directed and focused on the relevant areas of the organization.
So, let's continue with what you should do.
What Should You Do to Automate Compliance?
As a basic definition "automating compliance involves using technology and software solutions to streamline and facilitate the process of ensuring that an organization's activities align with relevant laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies."
In this context, we can highlight the areas to be included in a compliance automation project:
Automate Compliance Workflows: Utilize workflow automation tools to streamline compliance processes, such as policy management, risk assessment, incident response, access control, and audit tracking. Automation can help in assigning tasks, sending reminders, and tracking progress.
Implement Continuous Monitoring: Utilize automated monitoring tools to continuously track and analyze security events, anomalies, and potential threats. Real-time monitoring helps in identifying non-compliance and security incidents promptly.
Automate Evidence Gathering: Automating evidence gathering involves using technological tools and systems to streamline and simplify the business process of collecting and organizing various forms of documentation, data, logs, and records. The goal is to demonstrate compliance with specific requirements, regulations, or standards.
These automated tools enable the systematic retrieval, aggregation, and documentation of evidence from diverse sources within an organization, minimizing manual effort and enhancing efficiency in presenting a comprehensive and accurate picture of adherence to compliance mandates.
Automating compliance-related tasks, including recurring assessments and evidence gathering in audit preparation, improves data collection and audit readiness and ensures data is collected consistently and accurately.

What to Automate First?
Defining what to automate first in the context of automated evidence gathering involves a systematic approach to prioritize areas that will yield the most significant benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and risk reduction.
Here is a step-by-step process to determine what to automate first:
Conduct a Comprehensive Assessment: Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your organization's compliance requirements, processes, and existing evidence-gathering methods.
Identify Manual and Time-Consuming Tasks: Identify and document the manual and time-consuming tasks involved in evidence gathering. For example, these might include manual data entry, manual report generation, repetitive data collection from various sources, or manual correlation of evidence. Defining a score criteria to rank the controls based on time spent in evidence collection and verification can be a fantastic way to move forward.
Assess Risk and Impact: Assess the risks associated with each compliance requirement and the potential impact of non-compliance. Focus on high-risk areas where automation can significantly reduce the risk and improve compliance posture. Use the results of previous assessments to identify controls that might have failed and need more attention.
Consider Frequency and Volume: Evaluate the frequency and volume of evidence collection needed for different compliance requirements. Prioritize areas with high-frequency evidence-gathering needs or a large volume of data to be processed.
Analyze Complexity: Consider the complexity of evidence-gathering processes and identify tasks that are error-prone when done manually. Automate tasks that are straightforward to automate and prone to human error.
Prioritize Based on Return on Investment (ROI): Determine the potential return on investment (ROI) for each automation initiative. Evaluate the cost savings, time saved, risk reduction, and efficiency gains to prioritize initiatives that provide the highest ROI. Check this article to start learning about KPIs and KRIs.
These steps give you a comprehensive landscape of how to assess automation. As a result, you will be able to systematically determine the areas of evidence gathering that you should automate first based on the specific needs, risks, and potential for improvements.
With that information in your hands, you can start operationalizing automation.

Managing a Compliance Automation Project
Managing an automation project involves a structured approach to plan, execute, and oversee the implementation of automated processes. Likewise, identifying the right compliance automation tools and technologies is crucial, ensuring they align with the project's goals and organizational needs.
Engage Stakeholders
Engage with compliance stakeholders, including compliance officers, audit teams, and relevant department heads. For instance, you can gather their input on pain points and priorities related to evidence gathering, as their perspectives can guide prioritization. By actively involving these stakeholders, you can:
Identify Pain Points: Understand the challenges and pain points faced in the current evidence-gathering process. This feedback is invaluable for tailoring the automation solution to address these specific pain points effectively.
Gather Requirements: Gather detailed requirements and expectations for the automated system. Different stakeholders may have unique perspectives and requirements, so it is essential to gather a comprehensive set of inputs.
Prioritize Needs: Gain insights into the relative importance of various aspects of evidence gathering. Stakeholder input helps in prioritizing features and functionalities based on critical requirements and high-impact areas.
Foster Buy-In and Support: Involving stakeholders early and valuing their input fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the project. It increases buy-in and ensures that the automation project has the support it needs to succeed.
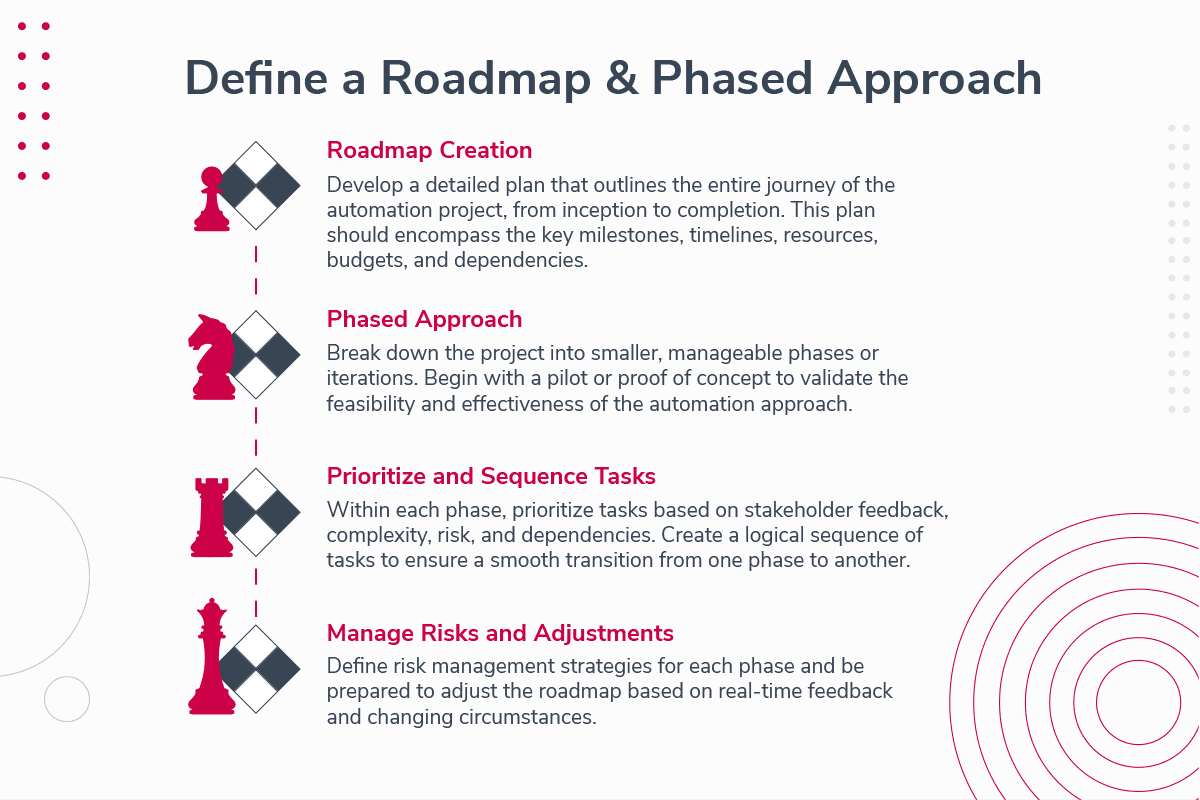
Define a Roadmap and Phased Approach
Develop a phased approach or roadmap for implementing automation in evidence gathering. Prioritize based on the assessments and considerations to outline a clear plan for gradual implementation.
Roadmap Creation: Develop a detailed plan that outlines the entire journey of the automation project, from inception to completion. This plan should encompass the key milestones, timelines, resources, budgets, and dependencies.
Phased Approach: Break down the project into smaller, manageable phases or iterations. Begin with a pilot or proof of concept to validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the automation approach.
Prioritize and Sequence Tasks: Within each phase, prioritize tasks based on stakeholder feedback, complexity, risk, and dependencies. Create a logical sequence of tasks to ensure a smooth transition from one phase to another.
Manage Risks and Adjustments: Define risk management strategies for each phase and be ready to adjust the roadmap based on real-time feedback and changing circumstances.
By effectively engaging stakeholders and following a phased approach, automation projects can progress in a structured manner. This allows you to address specific pain points, meet compliance requirements, and lead to a successful and impactful automation implementation.
Compliance Automation - Final Thoughts
Embarking on a strategic compliance journey needs meticulous scoping and informed decision-making. Scope, defined as the full set of work required to attain project objectives and deliverables, forms the fundamental groundwork. Specifically, it delineates the boundaries within which an organization's compliance efforts and controls are applied, ensuring a focused and directed approach.
The path to compliance automation begins with an understanding of why it's essential. Efficiency gains, streamlined workflows, and real-time monitoring underscore its significance.
Building upon this foundation, this second article navigates the "what" of automation, dissecting the critical areas to include in a compliance automation project. By prioritizing based on assessment and ROI, a roadmap is delineated, guiding a phased implementation that aligns with organizational goals.
Engaging stakeholders and fostering their involvement throughout this process is instrumental, ensuring collective insights steer the project toward success.
In conclusion, automation in compliance brings an era of streamlined processes, accurate data collection, and enhanced audit readiness, a transformation critical for modern enterprises navigating the complex landscape of regulations and standards.
Connect with our team to learn how StandardFusion can help you with compliance automation. Also, stay tuned for the next article to explore when is the right time to move forward and start the automation process.